Automatic Script Identification in the Wild
Abstract
With the rapid increase of transnational communication and cooperation, people frequently encounter multilingual scenarios in various situations. In this paper, we are concerned with a relatively new problem: script identification at word or line levels in natural scenes. A large-scale dataset with a great quantity of natural images and 10 types of widely-used languages is constructed and released. In allusion to the challenges in script identification in real-world scenarios, a deep learning based algorithm is proposed. The experiments on the proposed dataset demonstrate that our algorithm achieves superior performance, compared with conventional image classification methods, such as the original CNN architecture and LLC.
The SIW-10 Dataset
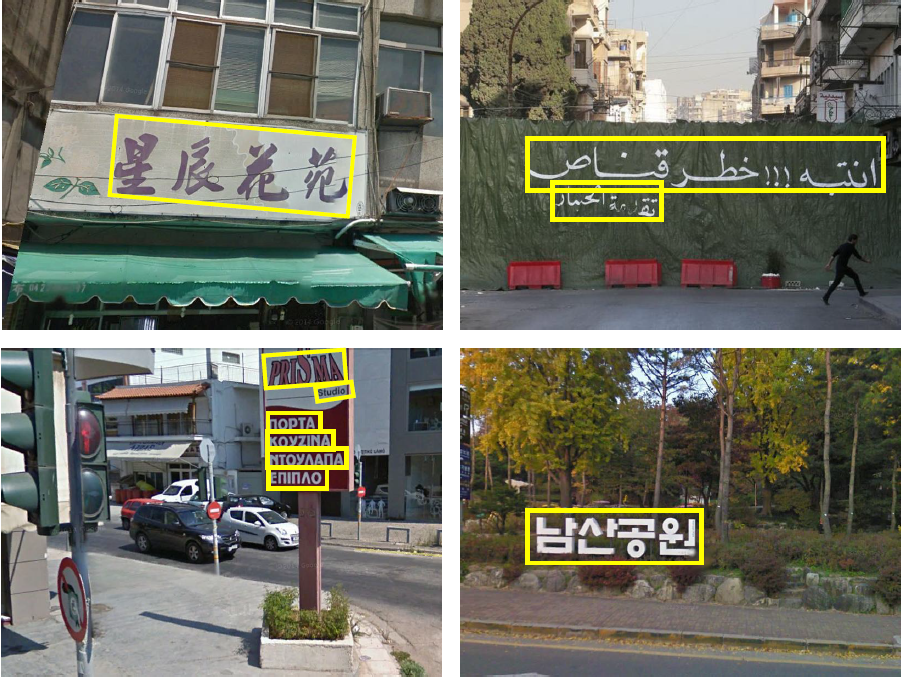
All together 13,045 multi-scripts text line images in 10 classes, cropped from 7,700 full images taken in-the-wild.

For collecting the dataset, we harvest a collection of street view images from Google Stree View and manually label the text regions by their bounding boxes. (See Fig. 2 for examples) Text line images are then cropped from these images. Only horizontally-written texts are included.

Method and Results
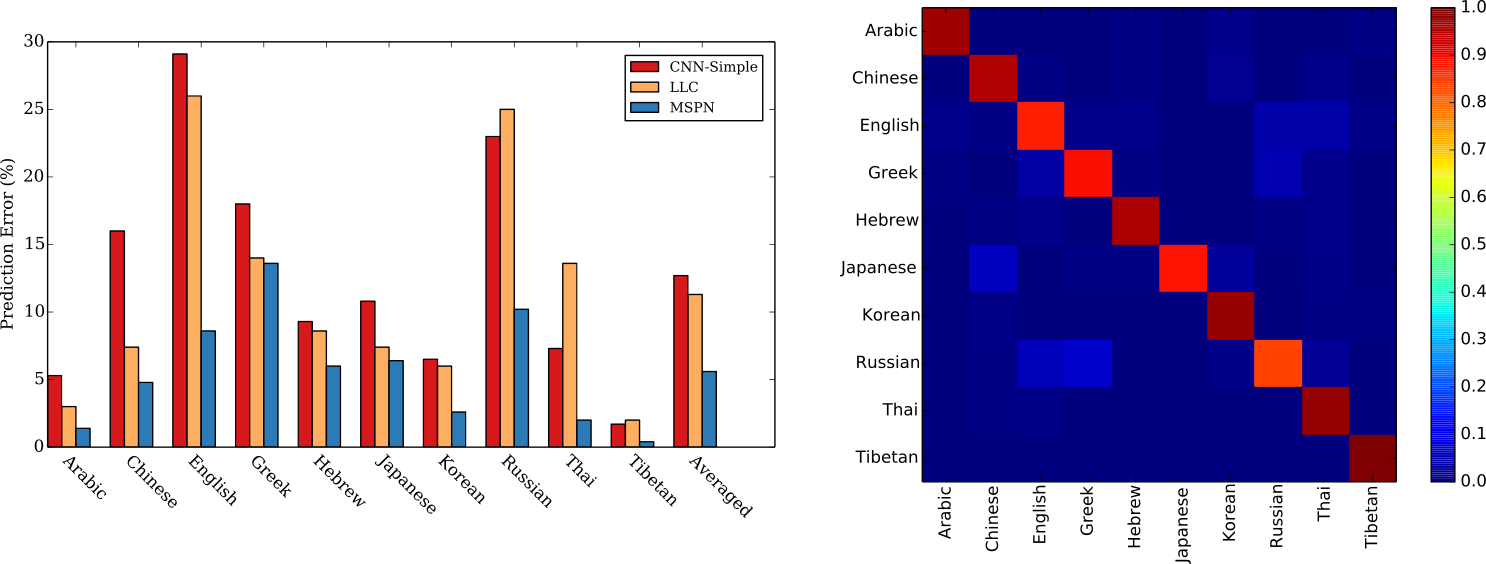
MSPN (Multi-stage Spatially-sensitive Pooling Network) is a deep learning method for script identification proposed in our ICDAR 2015 paper "Automatic Script Identification in the Wild". Results and comparisons on the SIW-10 dataset is shown below:
Tab. 1 Error rates comparisons among MSPN, CNN-Patch and LLC on SIW-10.
SIW-13
A dataset extended from SIW-10, proposed in [2]. Statistics of this dataset:
Download the dataset: SIW-13.zip
Citation
Please cite the paper if you find this dataset useful:
[1] Automatic Script Identification in the Wild [pdf]
Baoguang Shi, Cong Yao, Chengquan Zhang, Xiaowei Guo, Feiyue Huang, Xiang Bai
In Proceedings of ICDAR 2015 (oral presentation)
[2] Script Identification in the Wild via Discriminative Convolutional Neural Network
[pdf]
Baoguang Shi, Xiang Bai and Cong Yao
Pattern Recognition, to appear.
We would like to thank NVIDIA for GPU donations.
For questions about the dataset, please contact shibaoguang [AT] gmail [DOT] com.